Deploying Gaia Hub on Amazon EC2
Introduction
The template provided on this page provides an easy way to deploy a Gaia hub directly to Amazon EC2. You can use this template to deploy your own Gaia hub to your Amazon Web Services (AWS) account. Amazon EC2 is an affordable and convenient cloud computing provider. The template provides a one-click deployment for Amazon EC2 with either S3 or EBS as a storage provider.
Prerequisites
This procedure uses Amazon CloudFormation to configure an EC2 cloud computing provider to run the Gaia hub service with an S3 or EBS provider for file storage. You should have access to an AWS account either through your personal account or through a corporate account. This account should have permissions to create resources.
Additionally, you must also own a domain name and be able to update the DNS records associated with that domain name. The procedure on this page uses a free domain created on [freenom][https://www.freenom.com], generically the procedure used is similar to other domain name providers.
Launching the template
Use a link in the table to launch the CloudFormation template in the AWS region that you wish to deploy a Gaia hub.
| Template name | Description | Launch |
|---|---|---|
| Gaia Hub EC2 (us-east-1) | Deploys a Gaia hub service on EC2 with an S3 or EBS storage provider |
Task 1: Configure the CloudFormation template
Before launching your Gaia hub, you must configure the template with the appropriate values for your hub and the domain it runs on.
- Launch the template using the Launch stack button in the preceding table.
- Review the Prepare template and Template source fields to ensure that the fields contain template values.
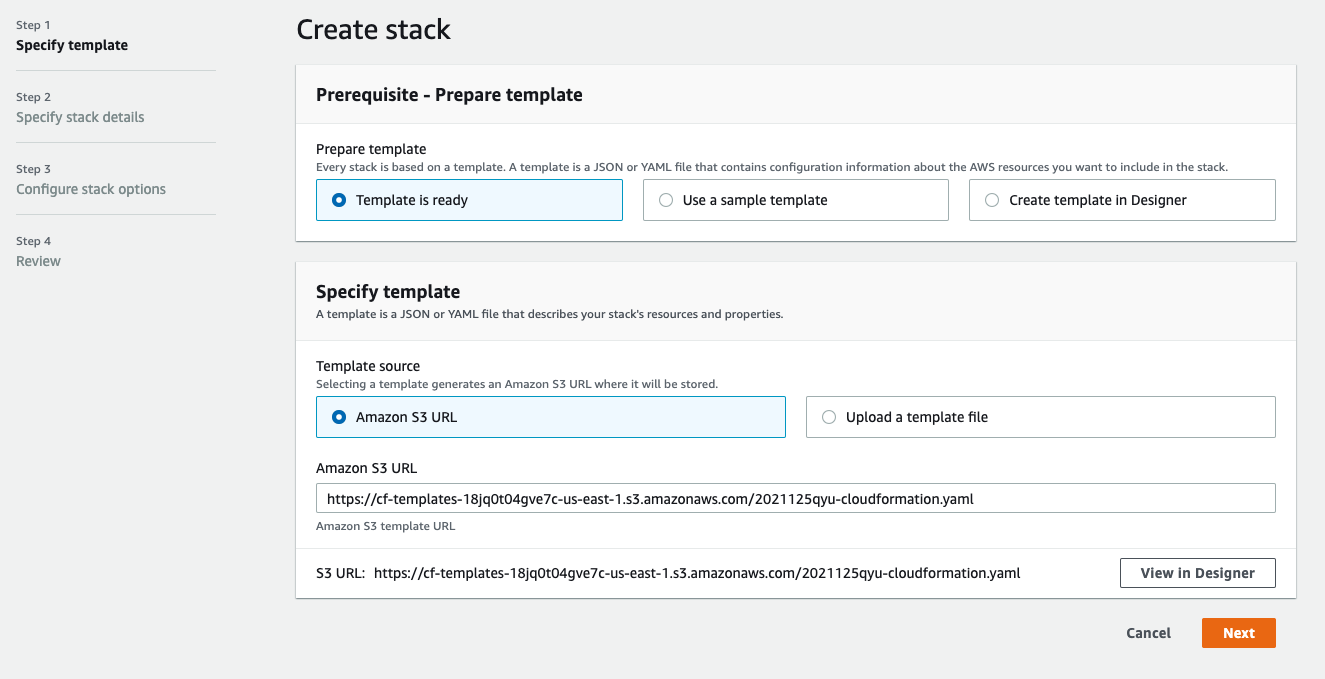
Click Next.
Specify configuration details for your Gaia hub:
i. Enter the Stack name. This name must be lowercase and unique within your AWS account.

ii. Enter the domain name on which the hub should run in the DomainName field. You must own this domain name and be able to update the DNS records associated with it.

iii. Enter an email address associated with the Gaia hub in the EmailAddress field. This should be a valid email that you have access to.

iv. Enter the name of the S3 bucket to create for data storage in the GaiaBucketName field. The template combines this name with the stack name to create a unique S3 bucket. The template ignores this field if GaiaStorageType is set to
disk.
v. Select the GaiaStorageType of which to use as a backend for the Gaia Hub. Selecting
s3causes the template to create an S3 bucket based on the name given in the previous step. Selectingdiskcauses the template to attach a separate EBS volume to the EC2 instance for Hub storage.vi. Select an available InstanceType from the drop-down. The default value is
t2.micro.vii. In the KeyName drop-down, select an EC2 KeyPair to enable SSH access to the EC2 instance. You should download the
.pemkeyfile for this pair from the EC2 console.For more information see the EC2 key pair documentation.

viii. Leave the SSHLocation field with the default value of
0.0.0.0/0to enable SSH access from any IP address. If you wish to restrict SSH access to the EC2 instance to a certain IP, you can update this field.ix. Select a public subnet and its associated virtual private cloud (VPC) from the SubnetId and VpcId drop-downs to designate where to deploy the Gaia hub instance.

Click Next.
Configure stack options for your Gaia hub:
i. Enter any key-value pairs you wish to include as tags for your Gaia hub. These are optional and display-only, they have no effect on the behavior of the CloudFormation stack.
ii. Select an IAM role for the Gaia hub. This is optional, if you don't specify am IAM role, the container runs with the same permissions as your AWS account.
Click Next.
Review the configuration of your Gaia hub, and make any changes necessary.
At the bottom of the page, select the checkbox to acknowledge that AWS may create IAM resources with custom names.
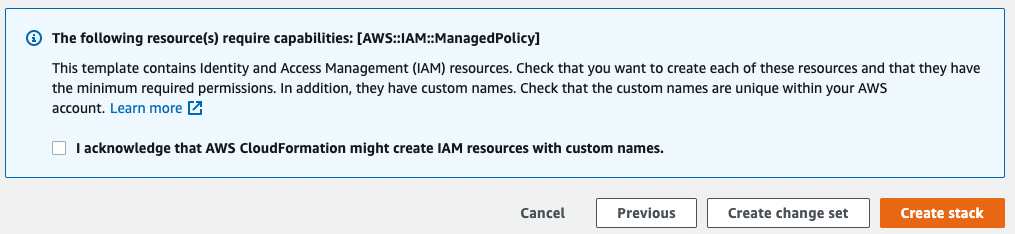
- Click Create stack to launch your Gaia hub. The AWS console displays the summary of the stack.
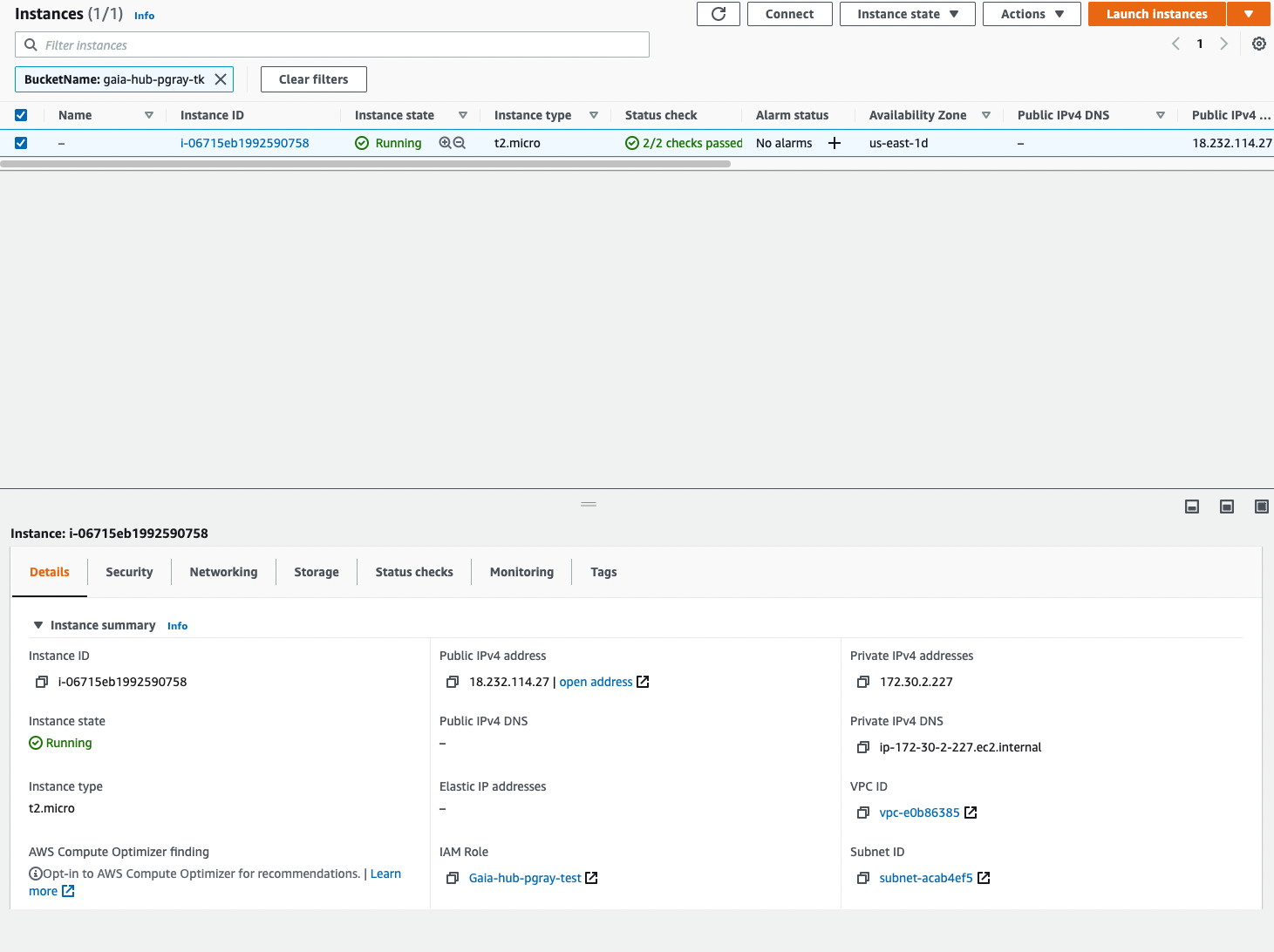
Task 2: Retrieve the public IP of your Gaia hub
Your stack can take several minutes to launch. You can monitor the Events tab of your hub to review the current progress of the launch. When the launch is complete, the Outputs tab displays information about the hub. Select the PublicIP and copy it to configure your domain name.
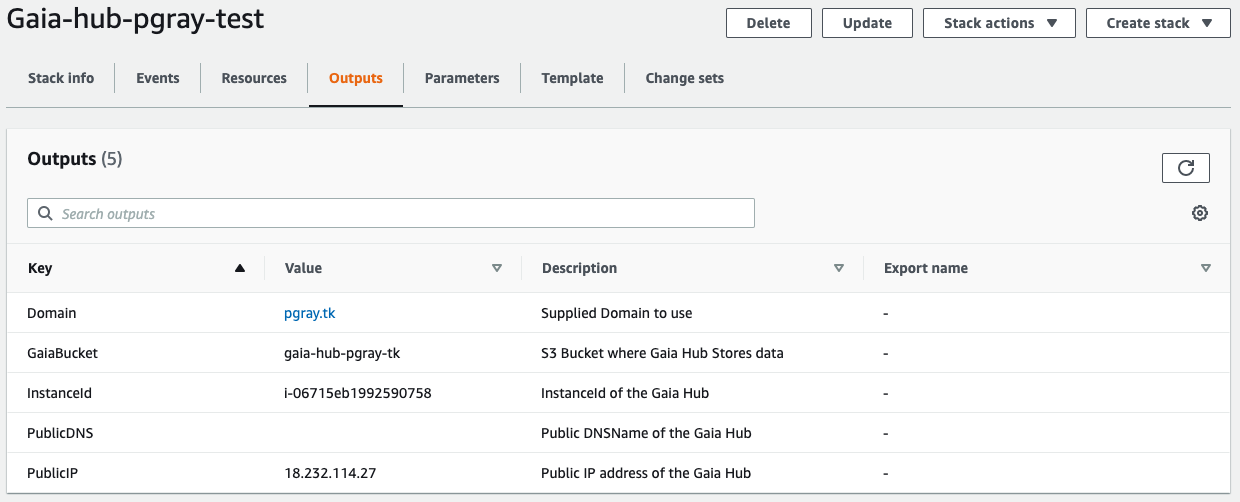
Task 3: Configure a domain name
Connect your domain to the Gaia hub EC2 instance by creating an A record for the domain DNS entry, and enter the
public IP from the previous step. In general, this procedure is similar depending on your hostname provider.
If you are using a free domain from freenom, use the following procedure:
- Log in to your freenom account.
- Under Services > My Domains, click Manage Domain next to the domain corresponding to your Gaia hub.

- Click Manage Freenom DNS in the tab bar.
- In the Add Records table, select
Afrom the Type drop-down, then paste the public IP of your Gaia hub EC2 instance in the Target field. - Click Save Changes to update the DNS record.
It can take up to 15 minutes for your DNS record changes to propagate. In a terminal, use the command
dig A +short <yourdomain.co> to review if the changes have propagated. If the output of this command is the container
public IP, the changes were successful.
Accessing your Gaia hub with SSH
To SSH into your Gaia hub EC2 host directly, you must have the keyfile used in container creation. Access the host with the following command in your terminal:
ssh -i <your keyfile.pem> admin@<public_ip_address>
Making changes to your Gaia hub
If you want to make changes to your Gaia hub, there are two options. You can delete the entire CloudFormation stack using the Delete button in the CloudFormation dashboard. Once you have deleted the stack, you can re-create one and modify your DNS to point at the new public IP.

To modify the instance in place, navigate to the EC2 instances console and type the instance name into the Filter instances field. Select the instance from the search suggestion, then click the instance to select it.
On the Tags tab, you can click Manage tags to update the relevant key value pairs for the instance. If you make changes to these tags, click Save, then select Reboot instance from the Instance state drop-down. Changes to the tags are only applied to the instance at reboot.